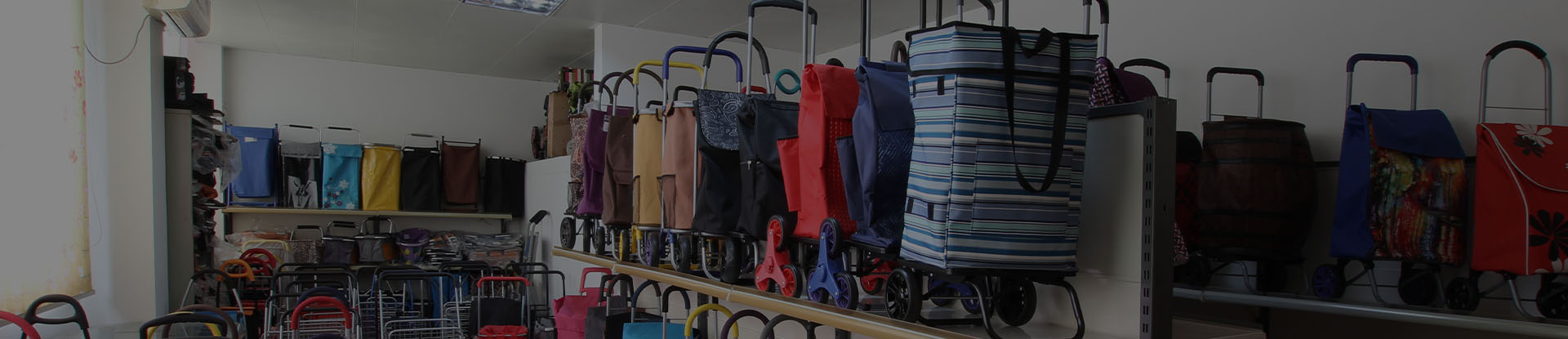
How Do Four-Wheel And Two-Wheel Foldable Shopping Carts Compare?
Foldable Shopping Carts have become indispensable for both households and businesses seeking portability, storage efficiency, and ease of transport. Among their various designs, two-wheel and four-wheel foldable carts are the most common. Each configuration offers distinct advantages depending on the user’s needs, surface conditions, and load requirements.
As a manufacturer committed to innovation and quality, WOCHANG designs both two-wheel and four-wheel foldable carts to serve a wide range of retail, logistics, and daily-use scenarios. Understanding their differences helps customers select the right model for maximum efficiency and comfort.
1. Structural Overview
The main difference between two-wheel and four-wheel Foldable Shopping Carts lies in their wheel configuration and frame balance.
Two-Wheel Carts:
Have one axle supporting two rear wheels. The cart must be slightly tilted backward to move, with the user carrying part of the load through the handle.
These are ideal for light to medium-duty use, such as carrying groceries or small packages.Four-Wheel Carts:
Include two front and two rear wheels that distribute weight evenly across the frame. They remain upright without tilting, offering higher stability and reduced effort when carrying heavier loads.
This type is commonly used in supermarkets, warehouses, and delivery operations.
2. Maneuverability and Handling
Two-Wheel Carts:
Offer greater agility in tight spaces and are easier to pull up stairs or curbs. Their design makes them suitable for urban environments or areas with uneven floors. However, since the user bears some of the load through the handle, they require more physical effort for heavier cargo.
Four-Wheel Carts:
Provide smoother rolling and better weight distribution. The cart remains balanced even when fully loaded, reducing strain on the user’s arms and back. Many models include swivel front casters for improved steering in aisles or narrow pathways.
Summary:
Two-wheel models emphasize portability and flexibility; four-wheel models focus on balance and comfort.
3. Load Capacity and Stability
| Type | Average Load Capacity | Stability Level | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Wheel Cart | 50–80 kg | Moderate | Small errands, groceries, home use |
| Four-Wheel Cart | 100–200 kg | High | Supermarkets, logistics, warehouse operations |
The four-wheel configuration allows for heavier loads because the weight is evenly distributed. It also minimizes the risk of tipping, especially when pushing across ramps or rough terrain. In contrast, two-wheel carts are best for lighter, more portable applications.
4. Folding Mechanism and Storage Efficiency
Both designs feature collapsible frames, but their folding methods differ slightly:
Two-Wheel Carts:
Often fold vertically with a simple hinge or telescopic handle. Their compact shape makes them easier to store in vehicles or closets.Four-Wheel Carts:
Typically fold horizontally or inward from the center, reducing both height and width. While slightly larger after folding, they remain space-efficient and easy to transport.
WOCHANG engineers each folding system with precision hinges and locking clips to ensure smooth operation and long-term durability.
5. Durability and Maintenance
Two-Wheel Models:
Have fewer components, meaning less maintenance and fewer potential mechanical failures. However, because they rely more on user balance and tilt control, wear may occur faster on the wheels and handle joints.
Four-Wheel Models:
Feature more moving parts such as swivel casters and connecting axles, requiring occasional cleaning and lubrication. The advantage is improved stability and smoother movement, even after years of heavy use.
Both types benefit from corrosion-resistant frames and reinforced joints. WOCHANG applies anti-rust coatings and uses industrial-grade fasteners to extend service life in indoor and outdoor environments.
6. Cost and Application Scenarios
Two-Wheel Foldable Carts:
Usually more affordable due to simpler construction and lighter materials. Best suited for personal shoppers, elderly users, or small-scale transport needs.Four-Wheel Foldable Carts:
Slightly higher in cost but offer greater functionality and comfort. Ideal for commercial buyers such as supermarkets, logistics companies, or delivery services requiring consistent heavy use.
From an operational perspective, investing in the right type can reduce fatigue, enhance efficiency, and improve long-term productivity.
7. WOCHANG’s Product Engineering Approach
At WOCHANG, design is driven by performance and user experience. Our two-wheel and four-wheel foldable carts share the following features:
Reinforced metal or aluminum frames for lightweight strength.
Ergonomic handles that reduce user fatigue during extended use.
High-quality wheels with sealed bearings for quiet and stable rolling.
Quick-folding mechanisms that enable compact storage and transport.
Optional accessories such as bottom trays, removable liners, and safety locks.
Each model is tested for load-bearing capacity, durability, and folding cycle performance to ensure long-term reliability.
Conclusion
The difference between four-wheel and two-wheel Foldable Shopping Carts lies in their design purpose and performance characteristics. Two-wheel carts are lightweight, compact, and best for light personal use, while four-wheel carts provide enhanced stability, higher capacity, and ease of maneuvering for commercial or heavy-duty tasks.
With years of manufacturing expertise, WOCHANG offers both solutions—engineered with precision, durability, and user comfort in mind—helping customers find the perfect balance between mobility, strength, and convenience.